Landscape of Climate Finance in Africa: Interactive Data Tools
The Landscape of Climate Finance in Africa provides the most comprehensive overview of climate investment flows in Africa. The project helps mobilize investment by creating a first-of-its-kind baseline for climate finance in Africa and identifies opportunities for replication and new products.
Scroll down ↓
At least nine times more climate finance is required in Africa. At USD 30 billion, current finance flows are only 11% of the USD 277 billion needed annually to implement NDCs and meet 2030 climate goals.
All sub-regions and countries received significantly less finance than their needs, with investment gaps varying across countries and regions.
Sixty percent of the total climate finance is concentrated in 10 countries.
While the remaining 40% is split among 45 countries.
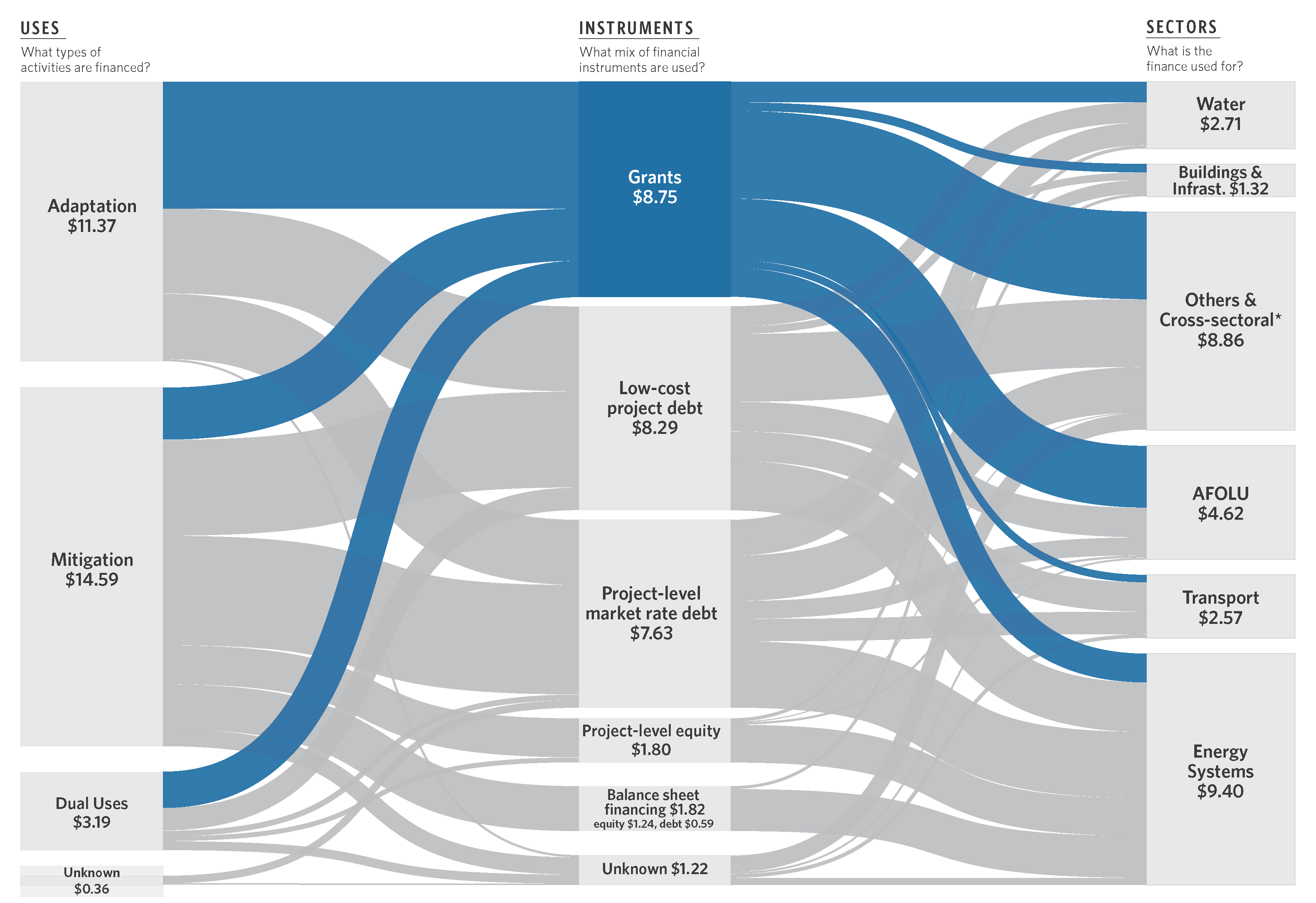
Public finance comprises 86% (USD 25 billion) of Africa’s tracked climate finance. The private sector, at 14% (USD 4.2 billion) needs to step up.
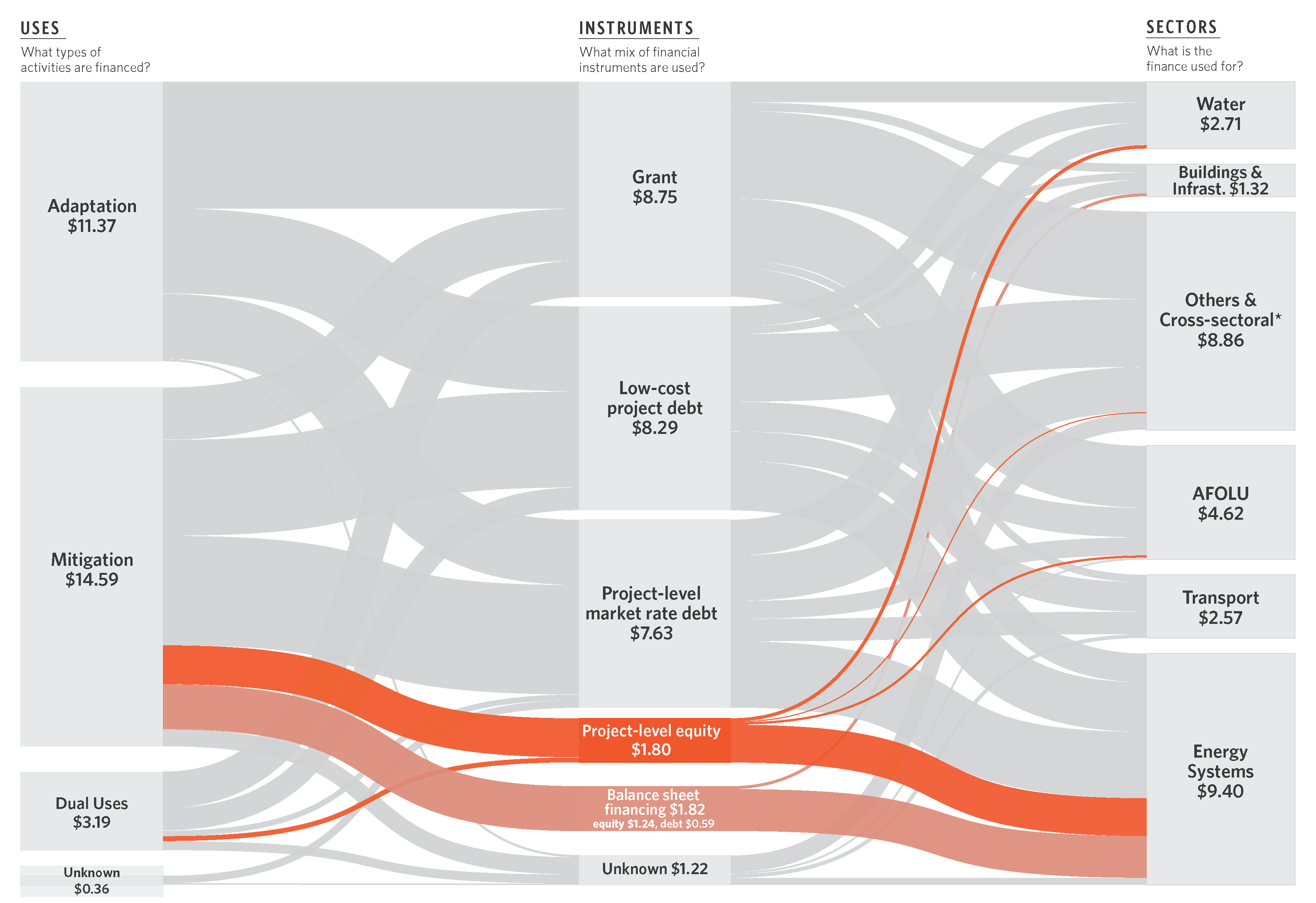
Private sector financing is much lower than in other regions like South Asia (38%), East Asia and Pacific (39%), and Latin America & Caribbean (48%).
Multilateral Development Financial Institutions are the largest sources of public climate finance. In the private sector, corporates are the largest source.
(Use the drop down above this diagram to switch views between public and private sources.)
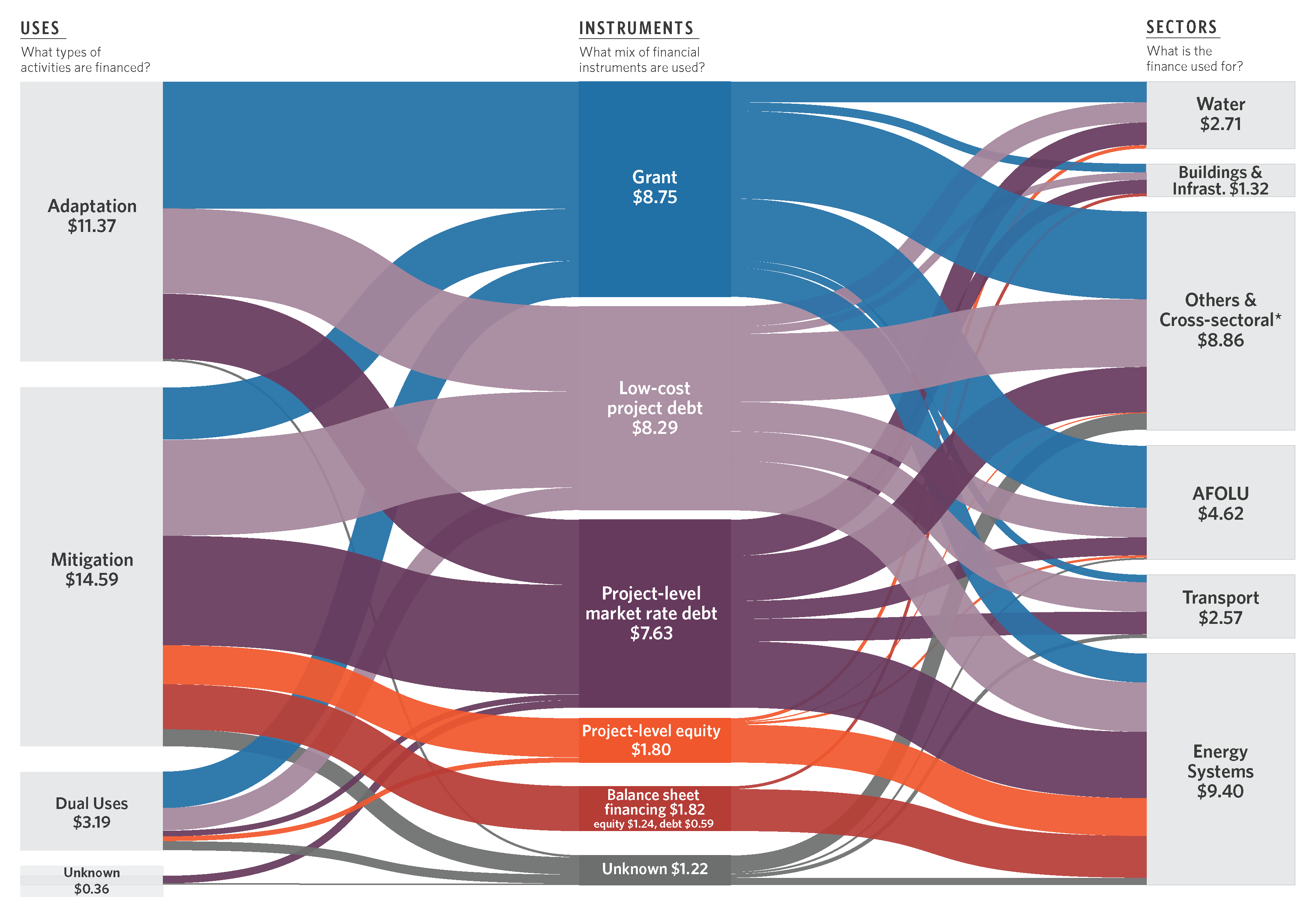
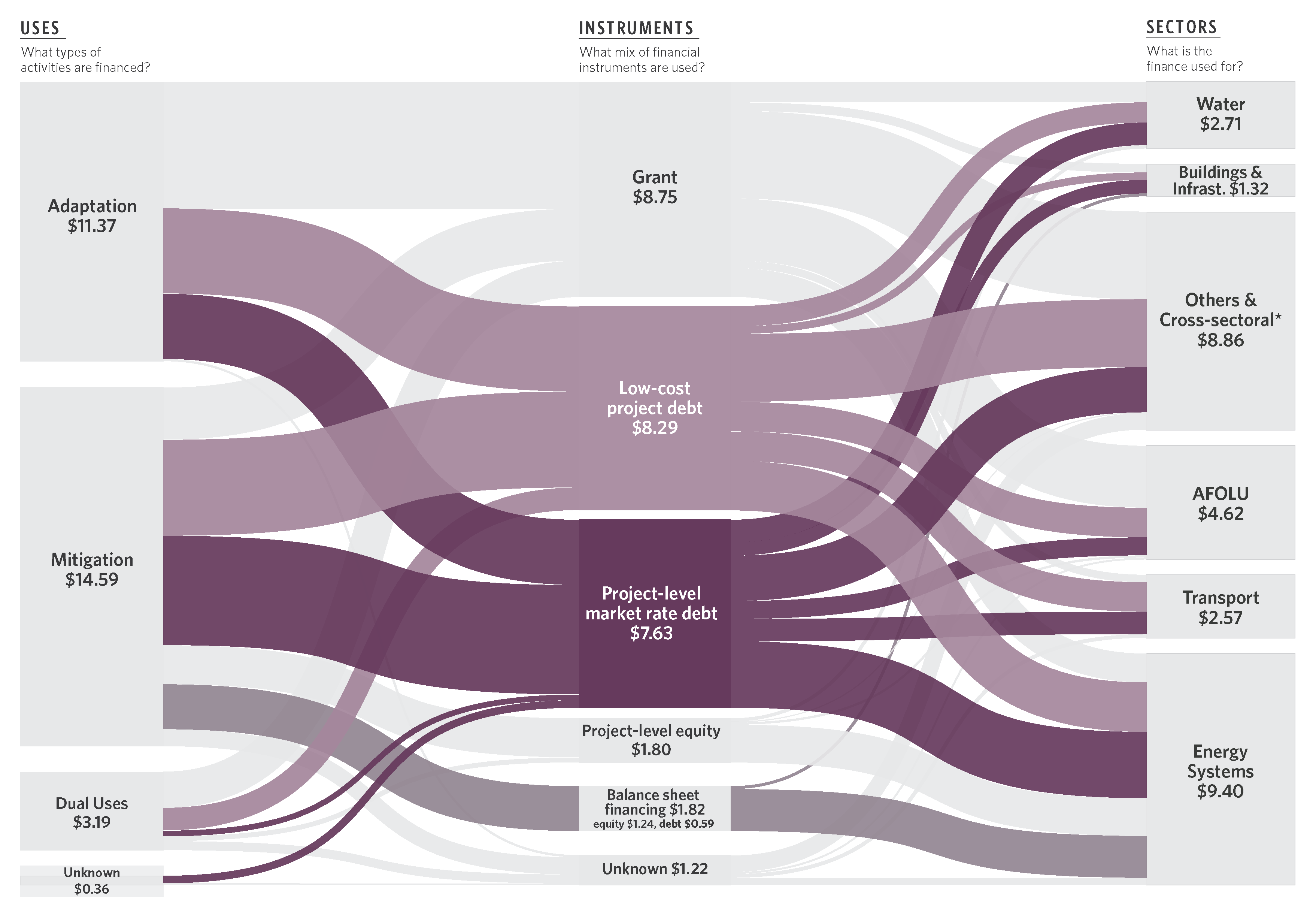
By sector, energy systems had the highest overall investment participation, at USD 9.4 billion. This is still only 7% of the estimated USD 133 billion annual investment needed to reach Africa’s clean energy goals. And pales in comparison to annual investments in fossil fuels (USD 29 billion) and government fossil fuel subsidies (USD 37 billion) in the region.
And despite the economic and social importance of the AFOLU sector, it received only 16% of the total climate finance in Africa. The AFOLU sector benefits from investments in other sectors, especially cross sectoral. However, investment still is significantly lower than the need, or commercial opportunity.
Africa’s future is urban. However, key sectors with high commercial potential that support urbanization have low private sector participation. For example, transport accounted for only 9% of total climate finance.
Tremendous opportunities exist to translate Africa’s climate goals into investment opportunities. By leveraging the data available here, and in our detailed report, policy and investment can be optimized to build a more resilient, secure, equitable, and low-carbon future for all African countries.
Continue scrolling to explore more interactive data, download the data, access graphics, or learn about our methodology.
Africa Climate Finance Dashboard Map
Interactive Sankey
Sector Trends