This publication is CPI’s analysis of Climate Adaptation Notes, an innovative climate finance instrument endorsed by the Global Innovation Lab for Climate Finance (the Lab). CPI serves as the Lab’s Secretariat. Each instrument endorsed by the Lab is rigorously analyzed by our research teams. High-level findings of this research are published on each instrument, so that others may leverage this analysis to further their own climate finance innovation.
Southern Africa—already one of the world’s most water-scarce regions—faces increasing intensity and frequency of severe drought, extreme precipitation, flash flooding, and water shortages.
Investments in water treatment and distribution, sanitation, water re-use, and wastewater treatment are urgently needed, but the public sector is limited in its ability to fund projects due to severely constrained government fiscal budgets. The COVID-19 crisis intensifies the need for improved water and wastewater infrastructure and exacerbates the public funding gap for those projects.
There is an abundance of private capital available in local debt capital markets, but these funds are not typically invested in infrastructure-related adaptation projects. A recent Intellidex report, however, indicates that that demand is growing: water-based solutions are now considered the highest priority sector for pension funds.
Climate Adaptation Notes is the first instrument to address water scarcity in Southern Africa by streamlining adaptation project financing into a single instrument through a partnership between commercial banks and institutional investors.
INNOVATION
Climate Adaptation Notes aims to increase the flow of funding into water and wastewater adaptation projects by combining construction financing and post-construction refinancing phases into a single instrument.
Combining short-term construction financing from commercial banks with long-term post-construction refinancing allows long-term funders to leverage the commercial banks’ construction project expertise, mitigating project performance risk and enabling investment in sectors previously seen as too risky by institutional investors. This new approach also reduces the time and cost involved in financing such projects and would enable climate adaptation projects to tap into the nearly USD 550 billion US domestic institutional savings pool in the region.
IMPACT
Based on a pilot issuance of USD 125 million targeting projects in Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia and South Africa, Climate Adaptation Notes could increase water and wastewater treatment capacity by approximately 90 megaliters per day, reaching an additional 90,000 or more municipal residents.
At scale, Climate Adaptation Notes could generate tens of millions of additional cubic meters of safely treated water and wastewater and could benefit hundreds of thousands of households facing water shortages and sanitation challenges.
DESIGN
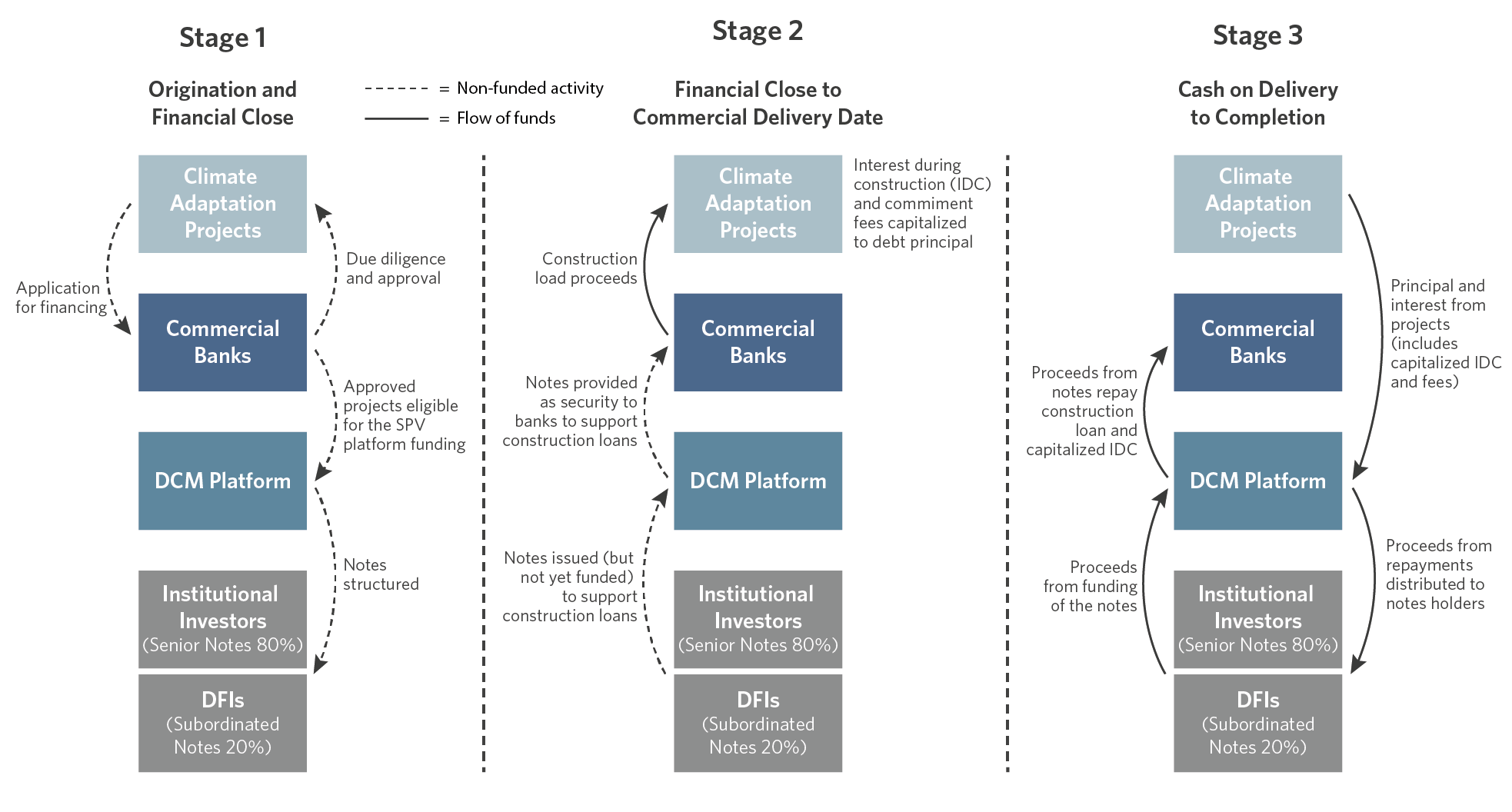
Climate Adaptation Notes works through a three-stage process, implemented through an independently managed and regulated Debt Capital Markets platform.
In Stage 1, the manager of the Platform works predominantly with local commercial banks to identify and screen suitable projects. Criteria for selection include commercial viability as well as adaptation criteria, to ensure projects reduce climate-related risk. Once selected, these projects are marketed to institutional investors and DFIs. No funding takes place at this point. Instead, the Notes represent a commitment to refinance the commercial bank construction loans after each project’s commercial operation date.
In Stage 2, commercial banks provide short-term construction loans. The commitment of the Notes allows the banks to provide more competitive loan pricing, as they have a commitment of refinancing and are therefore not subject to the capital costs imposed on commercial banks under Basel III for longer-term funding.
In Stage 3, after projects reach commercial operation, the Notes are funded. The proceeds are used to repay the short-term construction loans. The long-term investors assume the credit risk, and the projects benefit from the more favorable terms of the Notes.

