This publication is CPI’s analysis of Energy Savings Insurance, an innovative climate finance instrument endorsed by the Global Innovation Lab for Climate Finance (the Lab). CPI serves as the Lab’s Secretariat. Each instrument endorsed by the Lab is rigorously analyzed by our research teams. High-level findings of this research are published on each instrument, so that others may leverage this analysis to further their own climate finance innovation.
This report provides the analysis on Energy Savings Insurance, an instrument to insure the financial performance of energy efficiency savings projects in Mexico and other countries.
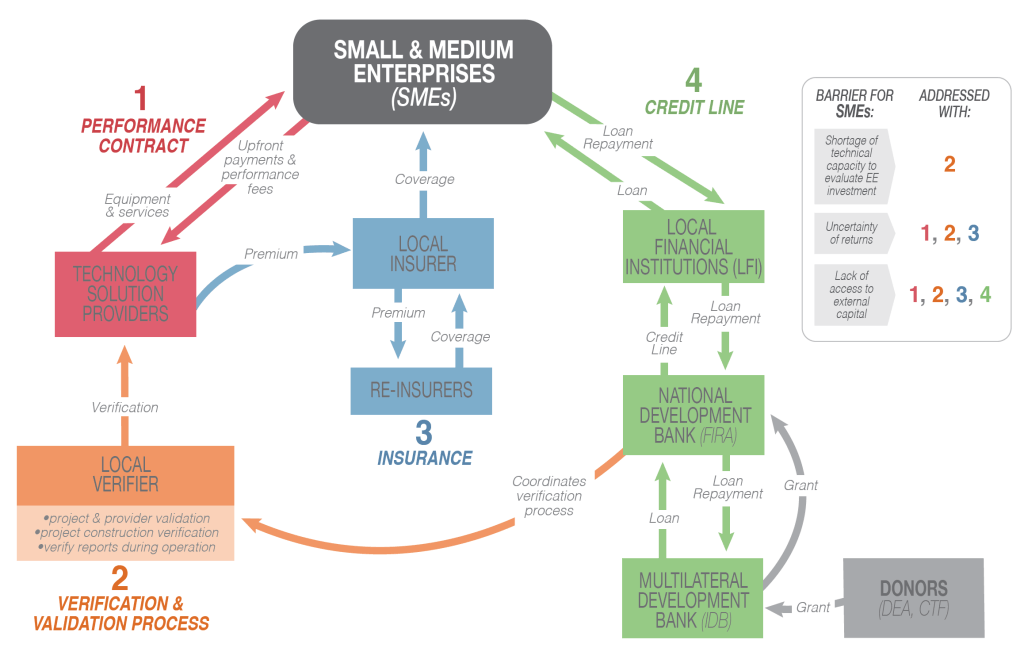
Energy efficiency upgrades can make small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) in developing countries more competitive and more productive, saving them money while reducing their emissions of harmful greenhouse gases. However, the market for such upgrades is typically limited to those with very short payback periods, such as lighting. This is particularly true for some developing countries and sectors. For example, in the SME sector, SMEs and local banks often lack both the technical capacity to assess the potential of more capital-intensive energy efficiency investments and the confidence that they will pay back, starving the sector of investment.
Energy Savings Insurance aims to address these investment barriers by paying out if the projected value of energy savings is not met. The Lab’s analysis shows that the instrument can absorb up to 80% of this underperformance risk.
Energy Savings Insurance insures the financial performance of energy efficiency savings projects. ESI now has projects in seven countries that will target thousands of businesses.
Energy Savings Insurance has been developed and led by the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), with the support of BASE, and with ongoing projects in seven countries. If implemented in all relevant developing countries, ESI will drive USD 10-100 billion in investment and provide annual emissions reductions of 27-234 MtCO2 by 2030.
- A pilot of the Energy Savings Insurance instrument is moving ahead in Mexico with a target to stimulate USD 25 million of investment in 190 energy efficiency projects in the agro-industry sector through 2020. The Inter-American Development Bank is implementing the pilot with local partners through funding from the Clean Technology Fund and the Danish Energy Agency.
- In Colombia, the pilot with BANCOLDEX was launched on June 1st 2016, with support from the Clean Technology Fund (CTF). The program aims to promote investments in energy efficiency in the hospital and healthcare sectors, and is expected to support 104 firms to reduce about 13,977 tCO2e/year.
- A pilot is being implemented in El Salvador with support from the Danish Energy Agency, BANDESAL, and grant resources from the Green Climate Fund. The program will target 500 firms investing in energy efficient projects and reducing about 37,500 tCO2e/year.
- In Nicaragua, Energy Savings Insurance is starting to structure its mechanisms with a national development bank for producers in the industrial, agricultural and forestry sectors.
- Energy Savings Insurance is being replicated in Brazil through three development banks, Bandes, BRDE and Fomento Goiás, and is currently in a market research phase.
- Energy Savings Insurance in Peru is being structured with a national development bank COFIDE, with potential targets including hotels, hospitals and clinics, food processing, fisheries, and textile.
Energy Savings Insurance continues to raise interest in other regions like China, Vietnam, Mongolia, the Caribbean, Chile, Mauritius, Turkey and India. The India Innovation Lab for Green Finance endorsed the concept for application in India in 2016. The ESI model is also being developed by BASE and partners in Italy, Portugal and Spain as part of a project titled ESI Europe, being funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.
Replicated on a global scale, Energy Savings Insurance can drive USD 10-100 billion in investment and provide annual emission reductions of 27-234 MtCO2 by 2030
DESIGN
The main components of the instrument are an insurance and package of complementary measures (see figure below).
Technology solutions providers will purchase the insurance to back their contractual guarantees to their SME clients on the performance of their energy efficiency products.
A package of complementary measures will address other barriers to investment such as technical capacity and access to capital. Measures include:
- Standardized contracts to reduce transaction costs, including a clause transferring part of the risk of underperformance to the technology solution provider
- Third party verification to ensure the quality of energy service providers and their projects
- Credit lines from development banks, which could provide long term capital, reducing the cost of financing projects
- Grant support to sustain market demand
More information: https://www.greenfinancelac.org/esi/